北京理工大学光电学院北京市混合现实与新型显示工程技术研究中心,北京 100081
融合几何光学的蒙日-安培方程方法和物理光学的迭代角谱算法,提出了一种复合型相位恢复方法。针对迭代角谱算法高度依赖初始值的问题,将蒙日-安培方程的解作为迭代初值,该初值通常比光强传输方程的解更准确。采用传统迭代角谱算法与混合输入输出算法的交替迭代策略,以避免算法过早陷入局部最优和迭代停滞。通过数值计算与仿真验证了所提复合型算法的优越性。
相位测量 相位恢复 蒙日-安培方程 迭代角谱算法 光强传输方程 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(5): 0512004
1 北京理工大学光电学院北京市混合现实与新型显示工程技术研究中心,北京 100081
2 北京理工大学光电成像技术与系统教育部重点实验室,北京 100081
3 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所空间光子信息新技术研究室,陕西 西安 710119
光源建模方法是光学仿真算法的核心之一,决定了仿真结果的精度。然而对任意面型的光源建模难度高,建模方法很少被公开讨论。本研究系统地介绍曲面光源建模方法。基于均匀性假设,对曲面光源的空间特性、方向特性进行统计学描述,给出采样光线参数应满足的概率密度函数和采样方法。对两个曲面光源实例进行建模,当采样光线数量在107量级时,建模结果在指定接收器上形成的辐照度分布与理论值间最大相对偏差在之内,建模精度很高。同时,分析了两种采样方法对曲面光源建模精度和速度的影响,可为曲面光源建模过程提供一定指导。
光学仿真 蒙特卡罗 光源建模 曲面光源 均匀采样 光学学报
2023, 43(21): 2122001
红外与激光工程
2023, 52(7): 20230430

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing Engineering Research Center of Mixed Reality and Advanced Display, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 MOE Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Imaging Technology and Systems, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
We implement Monte Carlo-based parallel ray tracing to achieve quick irradiance evaluation for freeform lenses with non-uniform rational B-splines (NURBS) surfaces. We employ the inverse transform sampling method to sample rays uniformly from the Lambertian light source and adopt the analytical form of the B-spline basis function to achieve fast surface interpolation. When performing parallel calculations for the intersections between the rays and the NURBS surfaces, we propose a parameter transformation method to avoid the parameters escaping from the defined range in the iteration process. Simulation results of two complex picture-generating freeform lenses show that our method is fast and effective.
propagation methods computation methods nonimaging optics lenses Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(5): 052201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing Engineering Research Center of Mixed Reality and Advanced Display, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Beijing Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Remote Sensing Technology, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
It is still very challenging to determine a freeform lens for converting a given input beam into a prescribed output beam where not only the irradiance distribution but also the phase distribution hardly can be expressed analytically. Difficulties arise because the ray mapping from the input beam to the output beam is not only intertwined with the required double freeform surfaces but also intertwined with the output phase distribution, whose gradient represents the directions of the output rays. Direct determination of such a problem is very difficult. Here, we develop a special iterative wavefront tailoring (IWT) method to tackle this problem. In a certain iteration, the current calculation data of the double freeform surfaces and the output phase gradient are used to update the coefficients of a Monge–Ampère equation describing an intermediate wavefront next to the entrance freeform surface. The solution to the wavefront equation could lead to an improved ray mapping to be used to update the corresponding phase gradient data and reconstruct the double freeform surfaces. In a demonstrative example that deviates much from the paraxial or small-angle approximation, the new IWT method can generate a freeform lens that performs much better than that designed by a conventional ray mapping method for producing two irradiance distributions in the forms of numerals “1” and “2” on two successive targets, respectively.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(9): 09001775
北京理工大学光电学院北京市混合现实与新型显示工程技术研究中心, 北京 100081
采用自由曲面透镜作为分束器以生成具有任意能量比的离散光斑阵列。根据能量守恒定律,将入射光束划分为一系列与光斑阵列对应的子区域。对于每个子区域,采用分离变量法计算子区域与相应光斑之间的光线映射关系,并采用最小二乘法构造遵循该映射关系的自由曲面。提供两个设计实例以检验自由曲面分束器的可行性:第一个设计可生成具有相同能量比例的高斯光斑阵列,第二个设计可产生具有预设不均匀能量比例的矩形平顶光斑阵列。仿真结果表明,考虑菲涅耳损耗后,两个设计实例的光输出比均高于89%。
光学设计 分束器 自由曲面光学 非成像光学 光学学报
2020, 40(17): 1722004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing Engineering Research Center of Mixed Reality and Advanced Display, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Tech-nology, Beijing, 100081, China
2 Beijing Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Remote Sensing Technology, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
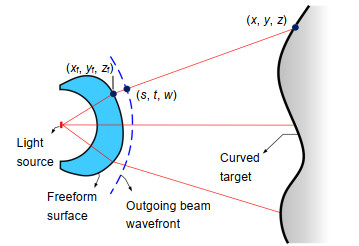
Current freeform illumination optical designs are mostly focused on producing prescribed irradiance distributions on planar targets. Here, we aim to design freeform optics that could generate a desired illumination on a curved target from a point source, which is still a challenge. We reduce the difficulties that arise from the curved target by involving its varying z-coordinates in the iterative wavefront tailoring (IWT) procedure. The new IWT-based method is developed under the stereographic coordinate system with a special mesh transformation of the source domain, which is suitable for light sources with light emissions in semi space such as LED sources. The first example demonstrates that a rectangular flat-top illumination can be generated on an undulating surface by a spherical-freeform lens for a Lambertian source. The second example shows that our method is also applicable for producing a non-uniform irradiance distribution in a circular region of the undulating surface.
freeform optics prescribed irradiance distribution curved target iterative wavefront tailoring Opto-Electronic Advances
2020, 3(7): 07200010
1 清华大学 电子工程系, 集成光电子学国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
2 清华大学 深圳研究生院, 半导体照明实验室, 广东 深圳 518055
基于非成像光学设计的自由表面光学系统,对提高以LED为核心的固态半导体照明的性能起着至关重要的作用。文章提出了简化模型模拟一次封装白光LED光源的色温角分布特性,并研究了自由表面光学系统对该色温角分布特性的影响。仿真与实验结果都表明,自由表面光学系统可以明显改善白光LED光源的色温角分布不均匀特性。
自由表面光学系统 色温 LED LED freeform optical system color temperature
1 清华大学电子工程系集成光电子学国家重点实验室/清华信息科学与技术国家实验室(筹), 北京 100084
2 清华大学深圳研究生院半导体照明实验室, 广东 深圳 518055
以发光二极管(LED)为核心的半导体照明光源成为世界公认的第三代照明光源。通常基于蓝光LED抽运黄色荧光粉产生白光的方案,因荧光粉的斯托克斯位移和宽光谱,其具有产业化价值的发光效率上升范围受到极大限制。另外,传统封装LED因其朗伯型发光分布和超高亮度会造成严重的眩光以及光分布难以满足照明应用要求从而导致光污染、光浪费,导致传统封装LED不能直接应用于通用照明领域。基于色度学原理,研究了半导体照明的极限流明效率,结果表明,基于红、绿、蓝三基色合成白光的方案,优化后在整个半导体照明白光区域显色指数Ra大于80,其极限流明效率可达430 lm/W,远远大于通常的蓝光LED与黄色荧光粉合成白光的方案。总结了在光学系统设计方面的系列成果:为使LED的配光满足应用要求,提出了基于分离变量的非成像光学系统设计理论以及为消除因光源的扩展性和法向矢量误差带来的照度分布偏移理想情况而引入的多种反馈迭代策略;面向道路照明,提出了按亮度设计自由曲面配光系统的方法,在保证照明参数满足标准的前提下,获得可实现最大的亮度/照度比的自由曲面光学系统;面向室内照明,利用非成像光学设计具有一体化微透镜结构的散光板,将类似于点光源的LED阵列转化为均匀柔和发光的面光源,大大降低了眩光,并引入模块化方案降低维修成本;面向特种照明,提出了由多个光学曲面构成的照度均匀的准直光学系统结构以及航标灯光源。
发光二极管 光学设计 非成像光学 极限流明效率





